Lithium-ion batteries, commonly known as Li-ion or Lithium batteries, are widely used in everyday life.
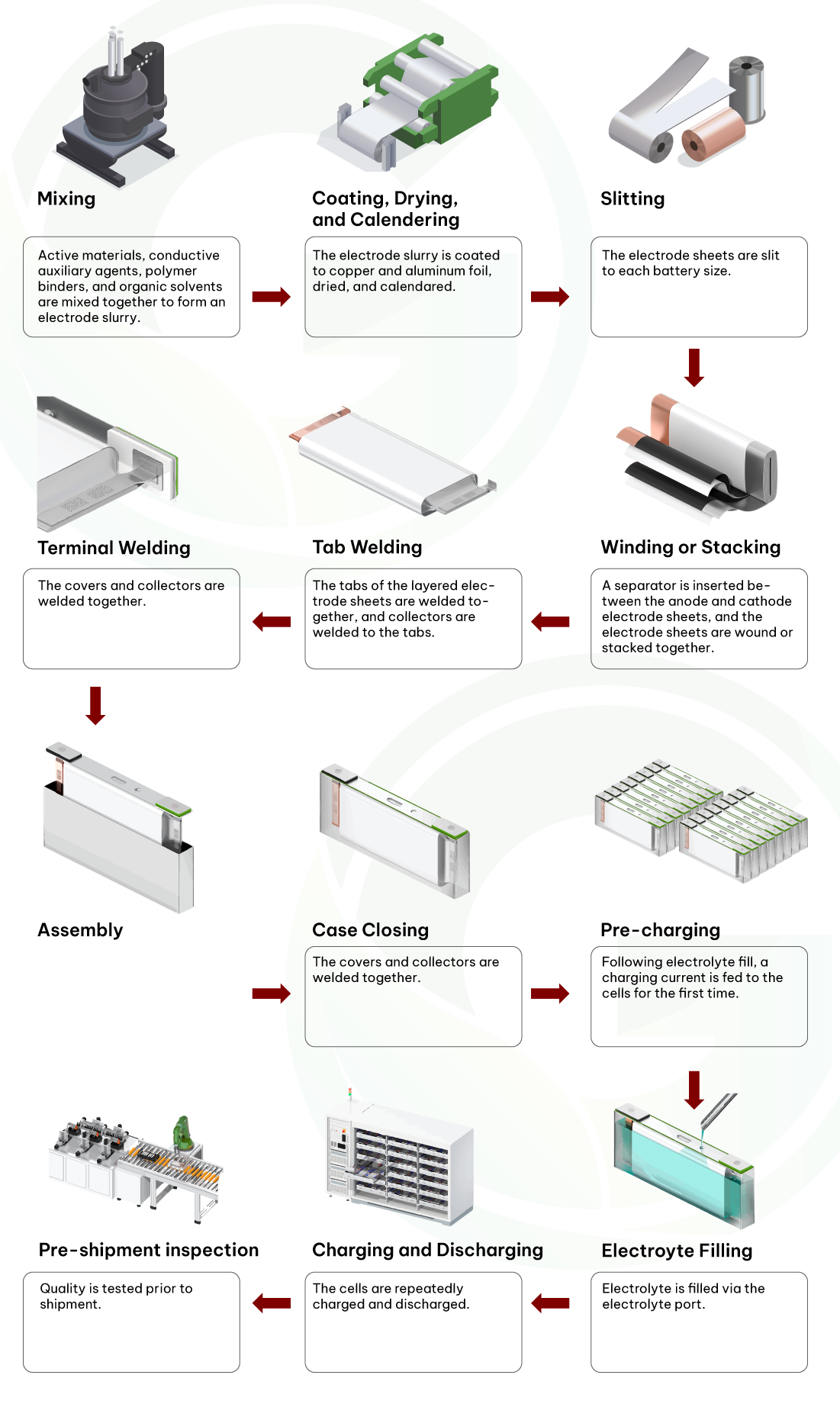
The production process of Lithium batteries involves 12 segments, ranging from material mixing to welding, drying, charging, discharging, etc. Ensuring adherence to the correct process and testing safety before shipment is crucial.
12-step Manufacturing Process of Lithium-ion Battery
Li-ion Battery Inspection and Testing Methods
-
- Lithium-ion Battery Insulation Resistance Testing
Structurally, it’ s necessary to keep the anode and cathode electrodes, as well as the electrodes and enclosure (case), insulated from each other. Failure to keep those components properly insulated—in other words, insufficient insulation resistance - could lead to a risk of ignition or fire accidents.
-
- Lithium-ion Battery Weld Quality Testing
If welds connecting tabs, collectors, and other battery components are insufficient, resistance between components will increase significantly, resulting in electrical energy loss and battery overheating. Such heating can reduce the battery’ s service life or cause fire.
-
- Monitoring of Battery Voltage and Temperature during Charge and Discharge Testing
Voltage and temperature are recorded during the charging and discharging test process in order to monitor changes in battery state. Recorded data is then analyzed to detect defects and rank batteries.
-
- Lithium-ion Battery Internal Resistance Testing
Although batteries’ internal resistance would ideally be zero, internal resistance exists due to a variety of factors. Internal resistance increases as a battery degrades.
-
- Lithium-ion Battery Open-circuit Voltage (OCV) Testing
A battery’ s voltage when it is not connected to any load is known as the open-circuit voltage (OCV). OCV values gradually decline due to self-discharge, a characteristic of batteries. When a battery has an internal defect, self-discharge increases, causing the OCV to decrease beyond the defined value.
After mass production, batteries are subjected to tests in laboratories to simulate altitude, fire resistance, crush resistance, temperature variations, vibration, shock, and overcharging, ensuring safety for end users.





